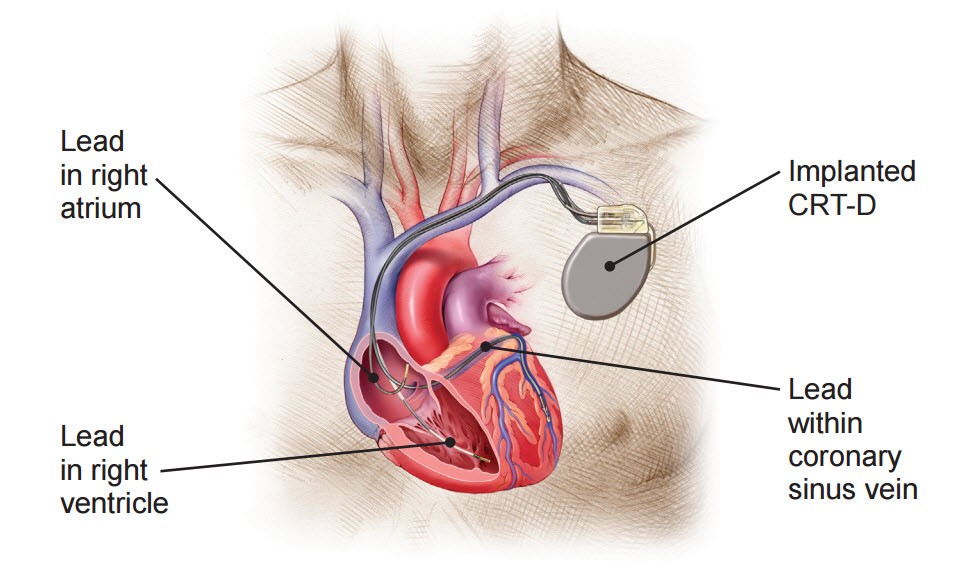
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT-D) involves implanting a device in the chest to arrange and efficiently cause the heart’s chambers to squeeze.
Biventricular pacemakers, also known as cardiac resynchronization devices, are used in cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) to provide electrical signals to both of the heart’s bottom chambers (right and left ventricles). The signals cause the ventricles to contract more precisely, which enhances the heart’s ability to pump blood.
In some cases, the device also includes an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), which can shock the patient’s heart back to a normal rhythm if it starts to beat dangerously irregularly.
Patients with heart failure whose lower heart chambers (ventricles) don’t contract in unison can receive treatment with cardiac resynchronization therapy. It is widely used for patients with left bundle branch block, a condition that causes heart failure, as well as for those whose low heart rates make cardiac pacing likely to be necessary.
The Top Cardiologist in Indore says your heart muscle is weaker if you have heart failure, which may prevent it from pumping out enough blood to sustain your body. If the chambers of your heart aren’t beating in unison, this could get worse.
Cardiac resynchronization therapy may lessen the signs and symptoms of heart failure as well as the danger of fatal consequences.

