Pericardiocentesis: An important medical procedure to remove fluid accumulated around the heart
Introduction
Pericardiocentesis is an important and lifesaving medical procedure used to remove excess fluid accumulated in the membranous sac surrounding the heart called the pericardium. This procedure becomes necessary when there is excessive fluid accumulation in the pericardium, which is medically known as pericardial effusion. The accumulation of this excess fluid can interfere with the normal functioning of the heart and can be life-threatening if not treated on time. Pericardiocentesis is an effective way to remove this fluid, helping the heart to return to normal functioning.
What is Pericardium and Pericardial Effusion?
The pericardium is a double membranous sac that surrounds the heart. This sac protects the heart and helps it to function safely. Under normal conditions, the pericardium contains a small amount of fluid, which is necessary for the smooth functioning of the heart. However, due to certain medical conditions, such as infection, inflammation, injury, or heart disease, the amount of this fluid may increase. The accumulation of this excess fluid stretches the pericardium and puts pressure on the heart, affecting the functioning of the heart. This is called pericardial effusion.
Purpose of Pericardiocentesis Procedure
The main purpose of pericardiocentesis is to remove the excess fluid accumulated in the pericardium so that the pressure on the heart can be reduced and its normal functioning can be restored. This procedure not only reduces the pressure on the heart immediately, but it also provides immediate relief to the patient and helps in avoiding possible complications.
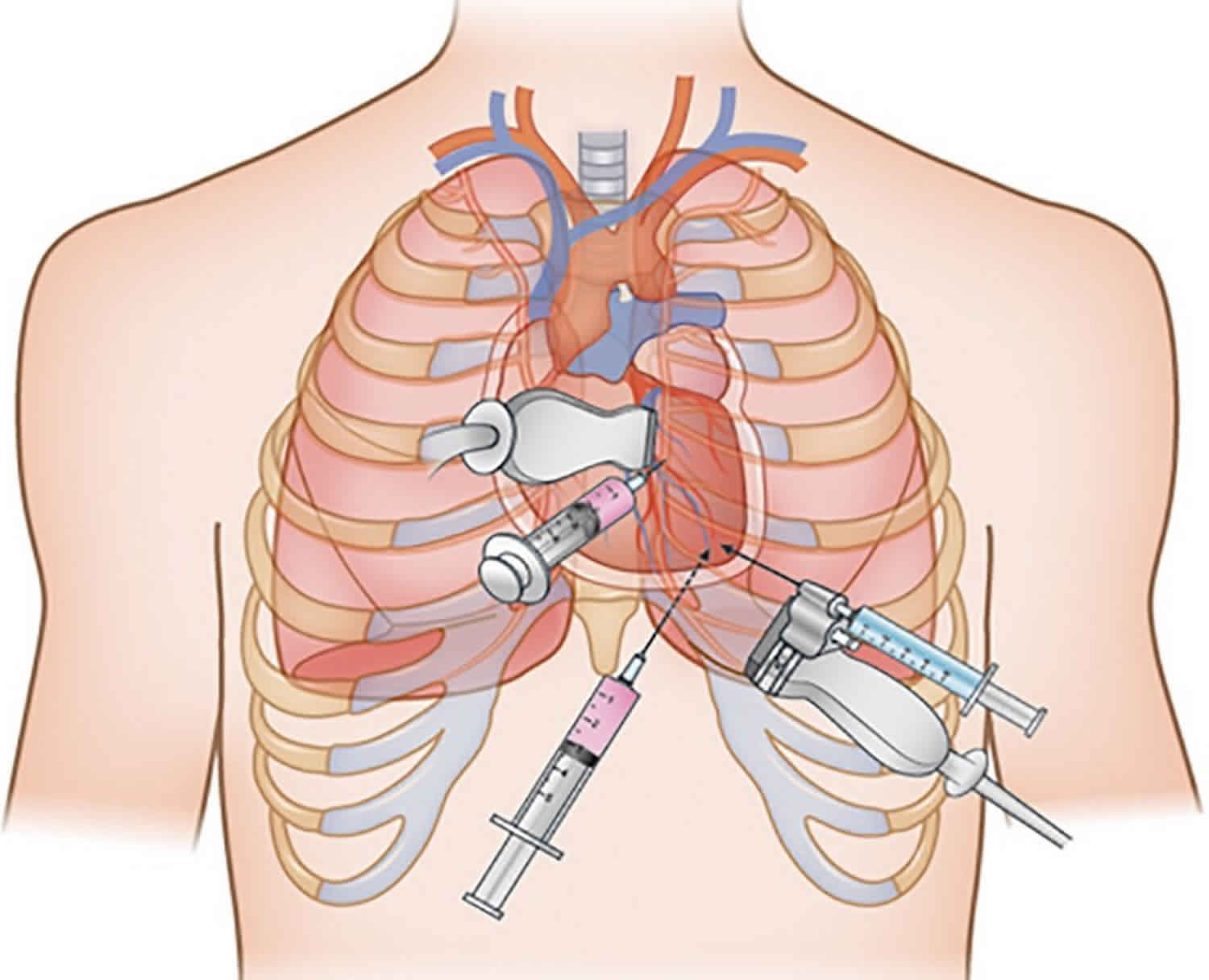
Procedure of Pericardiocentesis
Pericardiocentesis is a complex procedure, which requires expertise and extreme care. This procedure is usually performed in a specialized unit of the hospital, such as a cath lab or intensive care unit (ICU).
1. Preparation for the procedure:
1. First, the patient is given detailed information about the procedure, and his consent is taken.
2. The patient is placed in a comfortable position during the procedure, usually semi-reclining or on the back.
3. The chest area is cleaned and covered with a surgical drape to simplify the procedure and reduce the risk of infection.
4. The skin and surrounding areas are numbed using local anesthesia (local anesthetic) so that the patient does not feel any discomfort.
2. Use of the catheter:
1. A thin, flexible catheter tube is inserted into the pericardium with the help of a special needle.
2. During this procedure, doctors use imaging techniques such as ultrasound or fluoroscopy to guide the catheter to the correct location and avoid any complications.
3. Removal of fluid:
1. Once the catheter is in the correct position, the excess fluid is slowly drained out.
2. The fluid is collected in a special collection bag so that its quantity and properties can be assessed.
4. Analysis of samples:
1. The fluid removed is analyzed to determine the cause, such as infection, inflammation, cancer, or other heart conditions.
5. Post-procedure care:
1. After the fluid is removed, the catheter is removed and the area is covered with a bandage.
2. The patient’s condition is frequently assessed to ensure that the procedure was successful and that no complications have occurred.
Benefits of Pericardiocentesis
Pericardiocentesis has several important benefits, including:
1. Immediate relief:
This procedure immediately reduces the pressure on the heart, providing immediate relief to the patient.
2. Prevention of complications:
Performing pericardiocentesis on time can prevent potential complications, such as cardiac tamponade (excessive pressure on the heart), which is a serious condition.
3. Diagnosis:
By analyzing the fluid removed, doctors can find out the causes of fluid accumulation and plan treatment accordingly.
4. Non-surgical treatment:
Pericardiocentesis is a non-surgical procedure, which avoids the risks of surgery and makes it less complicated.
Risks and complications of pericardiocentesis
Although pericardiocentesis is a safe procedure, it can have some potential risks and complications, including:
1. Infection:
There may be a risk of infection at the site of catheter insertion, which antibiotics may be used to prevent.
2. Bleeding:
Bleeding may occur while inserting the catheter or while removing fluid, which must be managed immediately.
3. Injury to the heart or lungs:
If the catheter is not in the right direction while inserting, it may cause damage to the heart or lungs, which can be a serious complication.
4. Re-accumulation of fluid:
In some cases, re-accumulation of fluid may occur, which may require additional treatment.
Care after pericardiocentesis
Proper care and follow-up are essential after pericardiocentesis.

